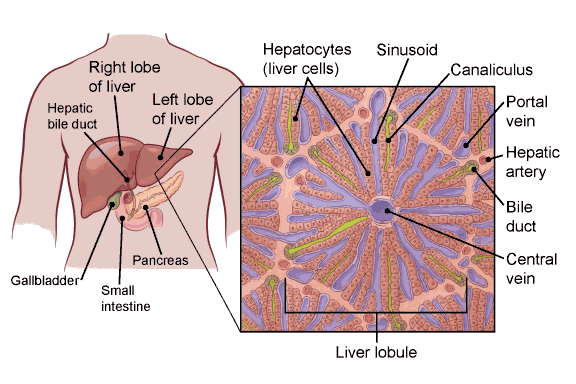
Hepatomegaly, also known as liver tumor, is the medical condition of having a large enlarged liver in patients
It is an umbrella term, having several different causes, that can generally be classified into non-cancerous hepatic tumors, liver cancer, or inflammatory liver disease. In some rare cases, liver tumor will present with jaundice or cirrhosis of the liver. In most cases, hepatitis occurs when the liver becomes enlarged due to damage done to liver tissues by infectious agents or excessive accumulation of bile acids.
Non-cancerous hepatic tumors, like acute hepatitis B virus (HBV) are quite common and can develop suddenly after receiving an injection. However, there are several causes of acute hepatitis B such as transfusion of blood plasma or organ transplantation.
Hepatoma is another rare form of liver cancer. It develops when cells in the liver divide abnormally. Unlike acute hepatitis B which spreads to other organs, hepatitis C, which develops slowly over time, usually presents with no symptoms.
Another form of cancer, liver melanoma, is caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun. A relatively rare type of this condition called chronic hepatitis C develops when the body's immune system does not produce enough natural defense mechanisms against the virus. Chronic hepatitis C is believed to be a genetically inherited form of the disease, since some people have a genetic predisposition for developing it.
Liver tumors can occur in any organ of the body, but their location is often related to the disease they affect. For example, adenomas, or liver tumor, are usually found in the liver, kidney, gallbladder, pancreas, and bile ducts, while pericardial mesotheliomas are usually found in the heart and lungs. Hepatocellular carcinoma is very common, as is hepatocellular abscess.
Pericardial Mesothelioma is a condition where the pericardium grows abnormally in the chest cavity. It can present with a mass of fluid in the chest cavity and is one of the most serious forms of this condition, especially if the pericardium is thickened and infected with polyps.
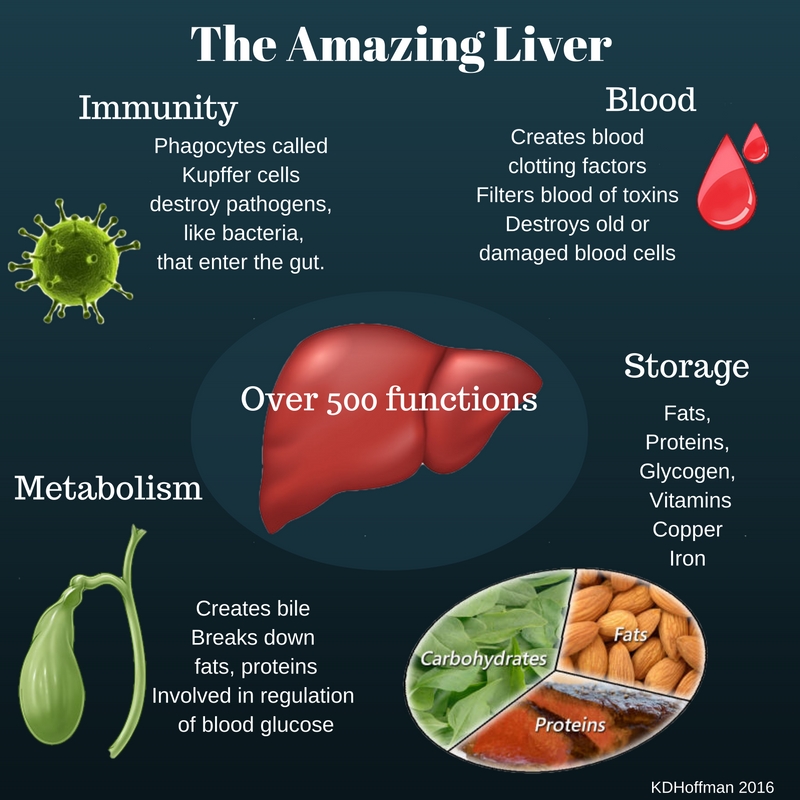
Hepatocellular Abscesses occur in the liver and are relatively rare but can be very dangerous
They can be fatal if not treated. If caught early, they can be removed surgically and cause no permanent damage to the liver.
Hepatocellular cancer can cause severe and irreversible damage to the liver, which makes them very difficult to cure. Patients with these types of malignancies have a very poor prognosis. In some cases, they may require immediate surgery and treatment to save their lives. However, if left untreated, they may be resistant to most other forms of therapy, including chemo-therapy, and it will be necessary to undergo a lengthy series of chemotherapy treatments.
The most common types of liver cancer are: non-small cell lung cancer (NSHCL), liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma), liver cancer (non-Hodgkin lymphoma), and pericardial mesothelioma. The most common symptoms of this type of cancer include vomiting, fever, and abdominal pain.
Liver cancer is rarely diagnosed by itself unless it affects someone who is in good health and has had a clean bill of health for at least a year prior to the cancer diagnosis. Most of the time, the doctor will see symptoms such as enlarged spleen, jaundice, fatigue, nausea, weight loss, nausea, or jaundice before considering a liver biopsy as the cause.
Liver cancer can be difficult to diagnose because it is generally located in an area of the liver that is difficult to access. A biopsy may show little if any tumor or no cancer tissue is present. This is why doctors often use a liver biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. A liver biopsy is performed when an abdominal ultrasound detects cysts in the liver, usually during an abdominal ultrasound.
Since the livers are rarely involved in the process of cancer removal, it is not uncommon for the patient to have surgery and radiation and chemotherapy combined. Chemotherapy and surgery are the standard treatment options in most cases, and often the first step is surgery. Chemotherapy is often combined with radiation and often the goal is to eradicate the cancer completely, so if a cure is not possible, chemotherapy is continued until the disease is in remission.