The amniotic fluid that is produced by the amnionic sac of an amniote is the primary fluid found within the amniotic sac
This fluid serves to facilitate the exchange of fluid, water, protein, and other biological products, but it also serves to protect the developing fetus from toxins and other harmful substances.
The abiogenic fluid is sterile and colorless. The fluid is produced through the process of amniocentesis, which is the process by which an amniotic sac is converted into the amniotic sac. The fluid usually develops at approximately one week after conception. However, this fluid does not typically develop until approximately two weeks after conception.
The abiogenic fluid is a clear liquid that is slightly warm in temperature. It is slightly darker than the amniotic fluid and is clear and odorless. The fluid does not contain any visible crystals, lumps, or pockets. The fluid has a sweet odor and is slightly sweet to the taste. This fluid is usually found in three different spots within the amniotic sac.
In amniocentesis, a small sample of the amniocentesis fluid is taken through a cannula and injected into the amniotic sac. The cannula can be used during amniogenesis. The fluid travels through the cervix, then it travels into the vagina. The amniocentesis fluid contains ammonium, which is a highly absorbable solid that absorbs and collects fluids.
The fluid inside the sac is mainly water because it contains ammonium, which is a solid that absorbs and collects fluids. When the fluid reaches the amniocentesis pouch it turns dark and will then start to separate into two separate pockets. Each pocket contains two different types of fluid:
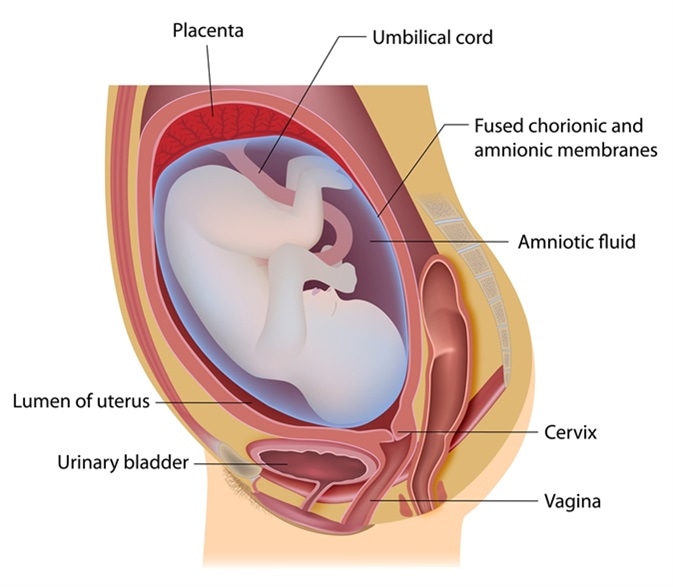
Amnioic fluid that accumulates inside the amniocentesis pouch is referred to as the intracellular fluid. In contrast, the extracellular fluid that is found outside the amniocentesis pouch is referred to as the extracellular fluid. In the external amniocentesis fluid, the fluid is colorless, clear, and has no odor. In the intracellular amniotic fluid, the fluid is colorless, greenish, has no smell, and is sticky.
The amniosaccharide is another type of fluid that accumulates inside the amniosaccharide. This fluid contains ammonium, which is a substance that is highly absorbable and collects fluid from the extracellular fluid. It is a colorless, creamy material. The amnion is a dark, slightly bitter smelling and odorless liquid that also accumulate in the amniosaccharide.
The amniocentesis fluid and the intracellular and extracellular fluids are then drained through the amniocentesis opening into the syringe. The fluid is then returned to the uterus through the cervix. The fluid is then drained back into the cavity of the uterus and then the amnion is removed.
There are some risks associated with amniocentesis. First, there is the possibility of pain relief. Secondly, the procedure can lead to a miscarriage of the fetus. Thirdly, pain may appear after the procedure.
One of the best ways to minimize the risks associated with this procedure is to schedule a home ultrasound scan to monitor your child's development. You can find a specialist to perform this procedure on you, or you can also find a home ultrasound specialist who can perform this procedure on your child. if you do not have access to a healthcare professional. Most amniocentesis clinics will allow you to perform the procedure at home.
Before having the procedure, you should talk to your healthcare professional if there is any other risk, such as infection or miscarriage. If you are pregnant or amniosaccharide is present, the procedure is not recommended. A doctor may recommend a hysterectomy to treat the infection. Your doctor may also recommend a procedure if you have endometriosis or polycystic ovary. Your gynecologist may also recommend this procedure if you are planning to become pregnant.