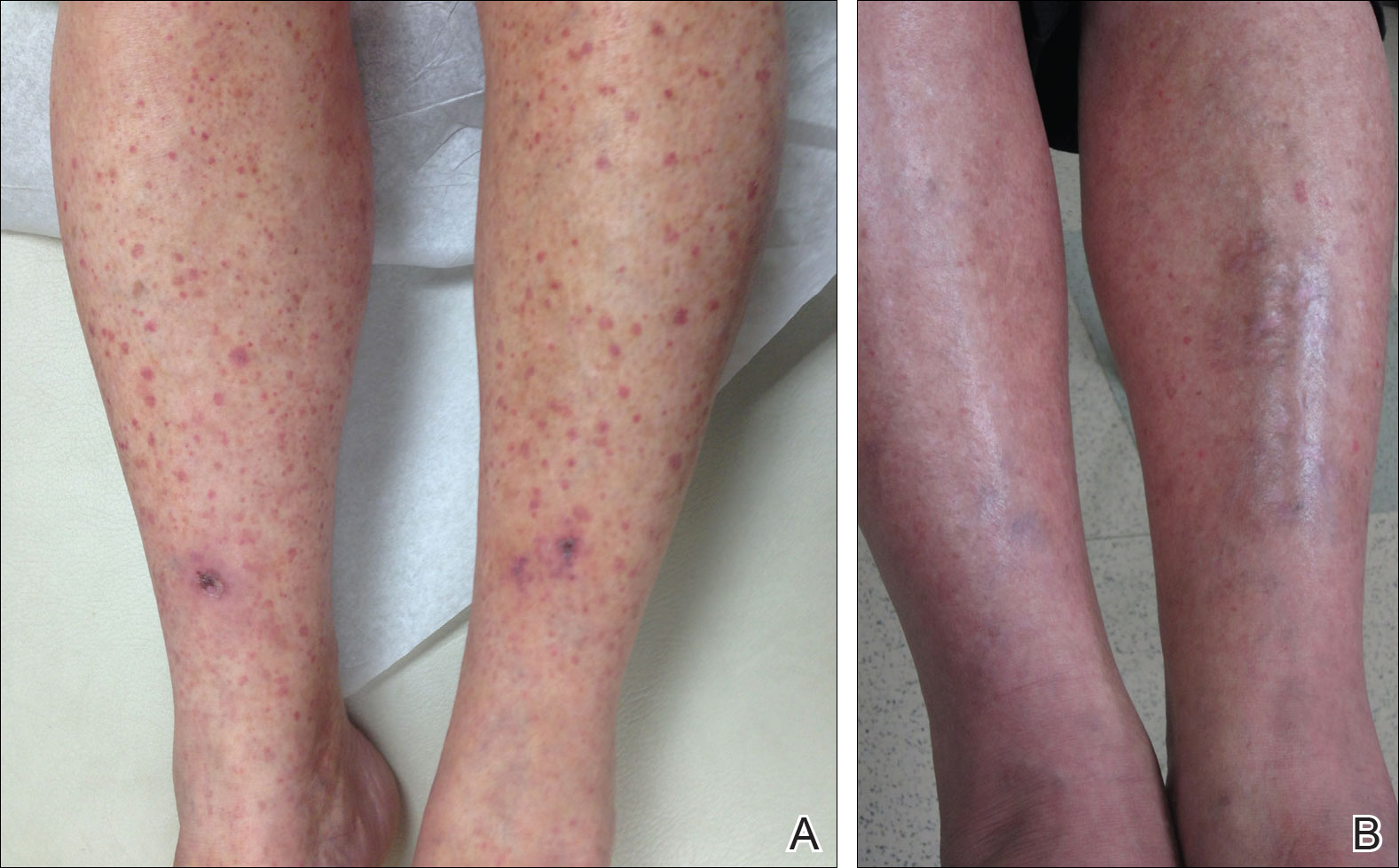
Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis is a form of arthritis and has a similar cause to that of rheumatoid arthritis. This type of arthritis causes deposits of fluid to collect within the joints of the body, which leads to inflammation. This form of arthritis is relatively common in adults between the ages of 30 and 60. Although it is not life threatening, this condition can lead to permanent disability if not treated properly.
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis occurs when the body's immune system attacks the joints of the body. The immune system identifies the cartilage as a foreign object, causing inflammation to occur. These deposits may then be filled with fluid, leading to increased pressure within the joints. If not treated, this condition can become very serious, resulting in swelling and possible infection. There are many ways in which leukocytoclastic vasculitis can be diagnosed, but the most common are through laboratory tests, x-rays, and MRIs.
Laboratory tests used to diagnose leukocytoclastic vasculitis are usually done to determine if there is an excess of protein in the blood that can be caused by a number of conditions. Sometimes the presence of an accumulation of protein in the blood is a sign of a more serious medical condition, so laboratory tests are usually used as a screening test. For example, a test called a neutrophil antibody response can be used to determine the presence of leukocytoclastic vasculitis. In this test, a protein is injected into neutrophils and the antibodies that bind to this protein in the blood are checked. If the antibodies are positive, this indicates that the patient has developed leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
X-rays can also be used to diagnose this condition, as abnormal amounts of fluid can be found in the joints, which can be easily seen on a scan. Ultrasound can also be used to check for fluid accumulation, as the fluid contains substances that can be seen under a microscope. Many patients with leukocytoclastic vasculitis undergo MRI. You can take a blood sample and then view the images from the MRI scans, and use the images to determine the level of fluid accumulation in the joints. After analyzing the MRI images, the diagnosis of leukocytoclastic vasculitis can be made.
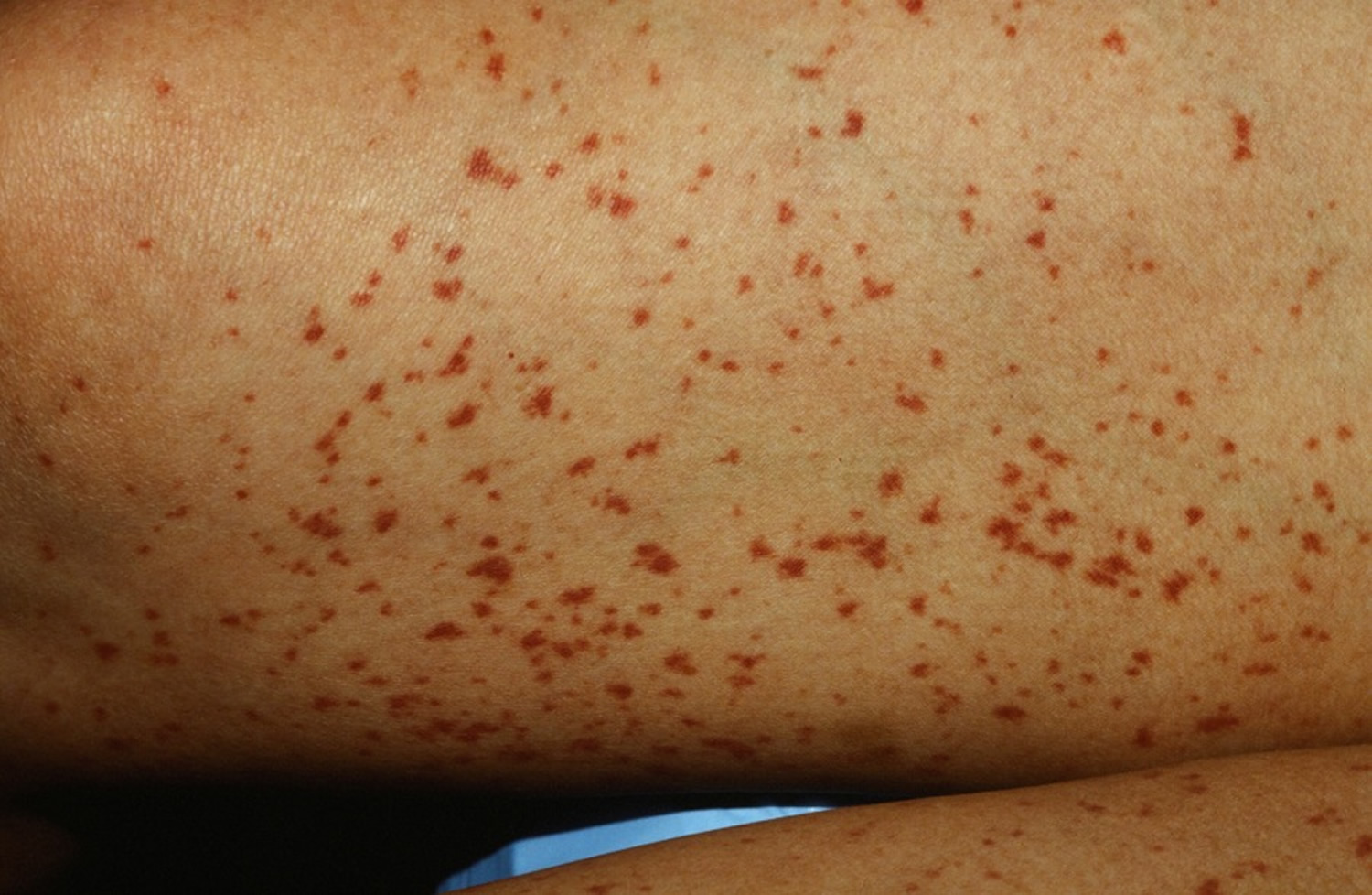
Although leukocytoclastic vasculitis is similar to rheumatoid arthritis, it can often be treated differently. This type of arthritis responds better to treatment because cartilage damage in the joints is not so severe. In addition, there is less swelling in the joints that are not affected, so medications taken to treat this condition have an easier effect on the joints. As with rheumatoid arthritis, treatment will depend on the severity of the leukocytoclastic vasculitis symptoms.
There are several treatment options for patients with this condition. These treatment options include steroids, anti-inflammatory drugs, antidepressants, and certain types of surgery. There are also several commonly used medicinal herbs that address the underlying cause by reducing pain, swelling, and inflammation.
Steroid medications are sometimes prescribed to help reduce pain, stiffness, and increase mobility in the joint. Anti-inflammatory medications such as prednisone can be prescribed to relieve joint swelling and reduce inflammation, while reducing inflammation, which can help to decrease pain. pain and reduce pain for some people.
Surgical procedures are also sometimes performed to treat this condition, although the exact procedures used are different from one another. For example, an osteotomy or a chondroplasty can be performed to relieve pain. It is important to speak with your doctor before undergoing any type of surgical procedure, especially if you are pregnant.